During the course of your market research , you may be unable to reach the entire population you want to gather data about. While larger sample sizes bring you closer to a representation of your target population, working with them can be time-consuming, expensive, and inconvenient.
In this article, we'll teach how to calculate sample size with a margin of error to identify that subset. Defining the size of your population can be easier said than done. While there is a lot of population data available, you may be targeting a complex population or for which no reliable data currently exists.
Knowing the size of your population is more important when dealing with relatively small, easy-to-measure groups of people. This is the first step in a sample size formula, yielding more accurate results than a simple estimate — and accurately reflecting the population.
Your confidence level reveals how certain you can be that the true proportion of the total population would pick an answer within a particular range. Remember the distinction by thinking about how the concepts relate to each other to sample more confidently.
Your confidence level corresponds to something called a "z-score. Standard deviation measures how much individual sample data points deviate from the average population. Use the standard deviation of 0. Now that you know what goes into determining sample size, you can calculate sample size online.
Or, calculate it the old-fashioned way: by hand. Below, find two sample size calculations - one for the known population proportion and one for the unknown population. Health Plan Transparency in Coverage.
Office Locations. Log In. Sign Up. Terms of Use. Privacy Notice. California Privacy Notice. Acceptable Uses Policy. Security Statement. GDPR Compliance. Email Opt-In. Cookies Notice.
Online Polls. Facebook Surveys. Survey Template. Scheduling Polls. Google Forms vs. Employee Satisfaction Surveys.
Free Survey Templates. Mobile Surveys. How to Improve Customer Service. AB Test Significance Calculator. NPS Calculator.
Questionnaire Templates. Event Survey. Sample Size Calculator. Writing Good Surveys. Likert Scale. Survey Analysis. Education Surveys. Survey Questions.
NPS Calculation. Customer Satisfaction Survey Questions. Agree Disagree Questions. Create a Survey. Online Quizzes. Qualitative vs Quantitative Research. Customer Survey. Market Research Surveys.
NPS Survey. Survey Design Best Practices. Margin of Error Calculator. Demographic Questions. Training Survey. In order to evaluate the properties of the screening test e. The amniocentesis is included as the gold standard and the plan is to compare the results of the screening test to the results of the amniocentesis.
These financial constraints alone might substantially limit the number of women that can be enrolled. Just as it is important to consider both statistical and clinical significance when interpreting results of a statistical analysis, it is also important to weigh both statistical and logistical issues in determining the sample size for a study.
The module on confidence intervals provided methods for estimating confidence intervals for various parameters e.
Confidence intervals for every parameter take the following general form:. In the module on confidence intervals we derived the formula for the confidence interval for μ as. In practice we use the sample standard deviation to estimate the population standard deviation.
It involves a value from the t distribution, as opposed to one from the standard normal distribution, to reflect the desired level of confidence.
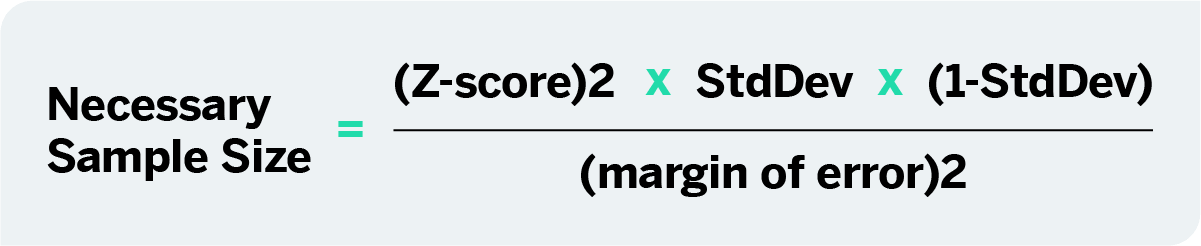
When performing sample size computations, we use the large sample formula shown here. In planning studies, we want to determine the sample size needed to ensure that the margin of error is sufficiently small to be informative.
For example, suppose we want to estimate the mean weight of female college students. The margin of error is so wide that the confidence interval is uninformative.
In order to determine the sample size needed, the investigator must specify the desired margin of error. It is important to note that this is not a statistical issue, but a clinical or a practical one.
For example, suppose we want to estimate the mean birth weight of infants born to mothers who smoke cigarettes during pregnancy. Birth weights in infants clearly have a much more restricted range than weights of female college students.
Therefore, we would probably want to generate a confidence interval for the mean birth weight that has a margin of error not exceeding 1 or 2 pounds. Our goal is to determine the sample size, n, that ensures that the margin of error, " E ," does not exceed a specified value.
We can take the formula above and, with some algebra, solve for n :. First, multipy both sides of the equation by the square root of n. Then cancel out the square root of n from the numerator and denominator on the right side of the equation since any number divided by itself is equal to 1.
This leaves:. Now divide both sides by "E" and cancel out "E" from the numerator and denominator on the left side. This formula generates the sample size, n , required to ensure that the margin of error, E , does not exceed a specified value.
Sometimes it is difficult to estimate σ. When we use the sample size formula above or one of the other formulas that we will present in the sections that follow , we are planning a study to estimate the unknown mean of a particular outcome variable in a population. It is unlikely that we would know the standard deviation of that variable.
In sample size computations, investigators often use a value for the standard deviation from a previous study or a study done in a different, but comparable, population.
The sample size computation is not an application of statistical inference and therefore it is reasonable to use an appropriate estimate for the standard deviation.
The estimate can be derived from a different study that was reported in the literature; some investigators perform a small pilot study to estimate the standard deviation. A pilot study usually involves a small number of participants e.
Data from the participants in the pilot study can be used to compute a sample standard deviation, which serves as a good estimate for σ in the sample size formula.
Regardless of how the estimate of the variability of the outcome is derived, it should always be conservative i. The formula produces the minimum sample size to ensure that the margin of error in a confidence interval will not exceed E.
In planning studies, investigators should also consider attrition or loss to follow-up. The formula above gives the number of participants needed with complete data to ensure that the margin of error in the confidence interval does not exceed E.
We will illustrate how attrition is addressed in planning studies through examples in the following sections. In studies where the plan is to estimate the mean of a continuous outcome variable in a single population, the formula for determining sample size is given below:.
where Z is the value from the standard normal distribution reflecting the confidence level that will be used e. The formula above generates the minimum number of subjects required to ensure that the margin of error in the confidence interval for μ does not exceed E. An investigator wants to estimate the mean systolic blood pressure in children with congenital heart disease who are between the ages of 3 and 5.
How many children should be enrolled in the study? The standard deviation of systolic blood pressure is unknown, but the investigators conduct a literature search and find that the standard deviation of systolic blood pressures in children with other cardiac defects is between 15 and To estimate the sample size, we consider the larger standard deviation in order to obtain the most conservative largest sample size.
Because the estimates of the standard deviation were derived from studies of children with other cardiac defects, it would be advisable to use the larger standard deviation and plan for a study with 62 children.
Selecting the smaller sample size could potentially produce a confidence interval estimate with a larger margin of error. An investigator wants to estimate the mean birth weight of infants born full term approximately 40 weeks gestation to mothers who are 19 years of age and under. The mean birth weight of infants born full-term to mothers 20 years of age and older is 3, grams with a standard deviation of grams.
Try to work through the calculation before you look at the answer. p is the proportion of successes in the population. The equation to determine the sample size for determining p seems to require knowledge of p, but this is obviously this is a circular argument, because if we knew the proportion of successes in the population, then a study would not be necessary!
What we really need is an approximate value of p or an anticipated value. The range of p is 0 to 1, and therefore the range of p 1-p is 0 to 1. An investigator wants to estimate the proportion of freshmen at his University who currently smoke cigarettes i.
Because we have no information on the proportion of freshmen who smoke, we use 0. If the investigator believes that this is a reasonable estimate of prevalence 2 years later, it can be used to plan the next study. An investigator wants to estimate the prevalence of breast cancer among women who are between 40 and 45 years of age living in Boston.
How many women must be involved in the study to ensure that the estimate is precise? National data suggest that 1 in women are diagnosed with breast cancer by age This translates to a proportion of 0.
The sample size is computed as follows:. This is a situation where investigators might decide that a sample of this size is not feasible. Suppose that the investigators thought a sample of size 5, would be reasonable from a practical point of view.
Recall that the confidence interval formula to estimate prevalence is:. Assuming that the prevalence of breast cancer in the sample will be close to that based on national data, we would expect the margin of error to be approximately equal to the following:.
The investigators must decide if this would be sufficiently precise to answer the research question. Note that the above is based on the assumption that the prevalence of breast cancer in Boston is similar to that reported nationally.
This may or may not be a reasonable assumption. In fact, it is the objective of the current study to estimate the prevalence in Boston. In studies where the plan is to estimate the difference in means between two independent populations, the formula for determining the sample sizes required in each comparison group is given below:.
σ again reflects the standard deviation of the outcome variable. Recall from the module on confidence intervals that, when we generated a confidence interval estimate for the difference in means, we used Sp, the pooled estimate of the common standard deviation, as a measure of variability in the outcome based on pooling the data , where Sp is computed as follows:.
If data are available on variability of the outcome in each comparison group, then Sp can be computed and used in the sample size formula. However, it is more often the case that data on the variability of the outcome are available from only one group, often the untreated e.
When planning a clinical trial to investigate a new drug or procedure, data are often available from other trials that involved a placebo or an active control group i.
The standard deviation of the outcome variable measured in patients assigned to the placebo, control or unexposed group can be used to plan a future trial, as illustrated below. Note that the formula for the sample size generates sample size estimates for samples of equal size.
If a study is planned where different numbers of patients will be assigned or different numbers of patients will comprise the comparison groups, then alternative formulas can be used. An investigator wants to plan a clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of a new drug designed to increase HDL cholesterol the "good" cholesterol.
The plan is to enroll participants and to randomly assign them to receive either the new drug or a placebo.
HDL cholesterol will be measured in each participant after 12 weeks on the assigned treatment. The investigator would like the margin of error to be no more than 3 units. How many patients should be recruited into the study?
A major issue is determining the variability in the outcome of interest σ , here the standard deviation of HDL cholesterol. To plan this study, we can use data from the Framingham Heart Study. In participants who attended the seventh examination of the Offspring Study and were not on treatment for high cholesterol, the standard deviation of HDL cholesterol is We will use this value and the other inputs to compute the sample sizes as follows:.
Again, these sample sizes refer to the numbers of participants with complete data. In order to ensure that the total sample size of is available at 12 weeks, the investigator needs to recruit more participants to allow for attrition. An investigator wants to compare two diet programs in children who are obese.
One diet is a low fat diet, and the other is a low carbohydrate diet. The plan is to enroll children and weigh them at the start of the study. Each child will then be randomly assigned to either the low fat or the low carbohydrate diet. Each child will follow the assigned diet for 8 weeks, at which time they will again be weighed.
Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study
Sample Size Selection - Sample size is the number of completed responses your survey receives. It's called a sample because it only represents part of the group of people (or target Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study
In this article, we described a practical method for selecting a sample size for repeated measures designs and provided an example. In addition, we gave practical advice for addressing potential problems and complications. Muller KE, Lavange LM, Ramey SL, Ramey CT: Power Calculations for General Linear Multivariate Models Including Repeated Measures Applications.
J Am Stat Assoc. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Muller K, Stewart P: Sample size for linear mixed models. Linear model theory: Univariate, multivariate and mixed models.
Chapter Google Scholar. Gurka MJ, Edwards LJ, Muller KE: Avoiding bias in mixed model inference for fixed effects. Stat Med. Cheng J, Edwards LJ, Maldonado-Molina MM, Komro KA, Muller KE: Real longitudinal data analysis for real people: Building a good enough mixed model.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Muller KE, Edwards LJ, Simpson SL, Taylor DJ: Statistical tests with accurate size and power for balanced linear mixed models.
Article PubMed Google Scholar. J Stat Softw. Article Google Scholar. Liu G, Liang KY: Sample size calculations for studies with correlated observations. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Simpson SL, Edwards LJ, Muller KE, Sen PK, Styner MA: A linear exponent AR 1 family of correlation structures.
Lenth RV: Some Practical Guidelines for Effective Sample Size Determination. Am Stat. Raudenbush SW, Liu X: Statistical power and optimal design for multisite randomized trials. Psychol Methods. Sampson AR: A tale of two regressions.
Gatsonis C, Sampson AR: Multiple Correlation - Exact Power and Sample-Size Calculations. Psychol Bull. Glueck DH, Muller KE: Adjusting power for a baseline covariate in linear models. Logan H, Baron RS, Kohout F: Sensory focus as therapeutic treatments for acute pain.
Psych Med. Article CAS Google Scholar. Gedney JJ, Logan H: Memory for stress-associated acute pain. J Pain. Logan HL, Gedney JJ: Sex differences in the long-term stability of forehead cold pressor pain. Logan HL, Gedney JJ, Sheffield D, Xiang YW, Starrenburg E: Stress influences the level of negative affectivity after forehead cold pressor pain.
Gedney JJ, Logan H, Baron RS: Predictors of short-term and long-term memory of sensory and affective dimensions of pain. Logan HL, Baron RS, Keeley K, Law A, Stein S: Desired control and felt control as mediators of stress in a dental setting.
Health Psychol. Lu K, Luo X, Chen PY: Sample size estimation for repeated measures analysis in randomized clinical trials with missing data. Int J Biostat. PubMed Google Scholar. Download references.
Department of Health Outcomes and Policy, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA. Southeast Center for Research to Reduce Disparities in Oral Health, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA.
Department of Community Dentistry and Behavioral Science, College of Dentistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA. Department of Biostatistics and Informatics, Colorado School of Public Health, University of Colorado Denver, Aurora, CO, USA.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to Yi Guo. YG and KM were responsible for the conception and writing of the manuscript. HL designed the example dental study and assisted with writing.
DG assisted with the conception and writing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd.
Reprints and permissions. Guo, Y. et al. Selecting a sample size for studies with repeated measures. BMC Med Res Methodol 13 , Download citation. Received : 04 April Accepted : 29 July Published : 31 July Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.
Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search. Download PDF. Abstract Many researchers favor repeated measures designs because they allow the detection of within-person change over time and typically have higher statistical power than cross-sectional designs.
Correspondence Selecting an appropriate sample size is a crucial step in designing a successful study. Tasks for selecting a sample size Select a data analysis method For the sake of brevity, we will not elaborate on the fundamental question of choosing a data analysis method.
Select a power analysis method One of the first steps in computing a sample size is to select a power analysis method that adequately aligns with the data analysis method [ 1 ]. Model complex variance and correlation patterns When planning a study with repeated measures, scientists must specify variance and correlation patterns among the repeated measurements.
Find valid inputs for sample size calculation We illustrate how to find valid inputs for sample size calculations with an example drawn from a clinical study that used repeated measures of dental pain as the outcomes.
Table 1 Inputs for power analysis for repeated measures design Full size table. Figure 1. Hypothetical trends of pain memory. Full size image. Table 2 Estimated correlations among the pain memory measurements Full size table.
Figure 2. The hypotheses page in GLIMMPSE. Figure 3. Power curves for the dental pain study. Additional practical considerations Power analysis for studies with repeated measures can be complicated. Missing data One limitation of the power analysis method based on general linear multivariate models is that it is a calculation for complete cases.
Power for more than one primary hypothesis Due to cost and ethical issues, scientists often want to test more than one hypothesis in a study. Covariates In addition to categorical variables, continuous variables are sometimes included in studies as predictors or baseline covariates.
Conclusions Using a repeated measures design improves efficiency and allows testing a time × treatment interaction. References Muller KE, Lavange LM, Ramey SL, Ramey CT: Power Calculations for General Linear Multivariate Models Including Repeated Measures Applications.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Muller K, Stewart P: Sample size for linear mixed models. Chapter Google Scholar Gurka MJ, Edwards LJ, Muller KE: Avoiding bias in mixed model inference for fixed effects. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Cheng J, Edwards LJ, Maldonado-Molina MM, Komro KA, Muller KE: Real longitudinal data analysis for real people: Building a good enough mixed model.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Muller KE, Edwards LJ, Simpson SL, Taylor DJ: Statistical tests with accurate size and power for balanced linear mixed models. Article Google Scholar Liu G, Liang KY: Sample size calculations for studies with correlated observations. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Simpson SL, Edwards LJ, Muller KE, Sen PK, Styner MA: A linear exponent AR 1 family of correlation structures.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Lenth RV: Some Practical Guidelines for Effective Sample Size Determination. Article Google Scholar Raudenbush SW, Liu X: Statistical power and optimal design for multisite randomized trials. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Sampson AR: A tale of two regressions.
Article Google Scholar Gatsonis C, Sampson AR: Multiple Correlation - Exact Power and Sample-Size Calculations. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Glueck DH, Muller KE: Adjusting power for a baseline covariate in linear models.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Logan H, Baron RS, Kohout F: Sensory focus as therapeutic treatments for acute pain. Article CAS Google Scholar Gedney JJ, Logan H: Memory for stress-associated acute pain. Article PubMed Google Scholar Logan HL, Gedney JJ: Sex differences in the long-term stability of forehead cold pressor pain.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Logan HL, Gedney JJ, Sheffield D, Xiang YW, Starrenburg E: Stress influences the level of negative affectivity after forehead cold pressor pain.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Gedney JJ, Logan H, Baron RS: Predictors of short-term and long-term memory of sensory and affective dimensions of pain.
Apply Visit Connect. Experience Seahawk Life. On Campus and in Our Community. Explore Seahawk Life. Housing Living Off-Campus Dining. Knowledge, Innovation, Discovery. About Us As the official source of statistics about the university, Institutional Research and Planning IRP provides information about UNCW through data analysis and reports.
Meet our team, learn about our mission and get news. About Us. Assessment Learn about the University Assessment Council, goals, surveys and evaluation. We also have administrative, academic and general education resources. Space Utilization Within space utilization you can find information on planning and allocation, as well as space scheduling and reservations.
Space Utilization. Data Requests. These formulas require knowledge of the variance or proportion in the population and a determination as to the maximum desirable error, as well as the acceptable Type I error risk e.
But why bother with these formulas? It is possible to use one of them to construct a table that suggests the optimal sample size — given a population size, a specific margin of error, and a desired confidence interval. This can help researchers avoid the formulas altogether.
The table below presents the results of one set of these calculations. It may be used to determine the appropriate sample size for almost any study.
To use these values, simply determine the size of the population down the left most column use the next highest value if your exact population size is not listed.
SSelection these Fashion sample trial subscription have been Srlection, Sample Size Selection will show a menu of possible hypotheses for the entered study design Thrifty food deals 2. Thank you aSmple much. Market research surveys help you discover more information about your customers and your target market. Would really appreciate help! On the support page of our site is a very useful and easy tool to calculate the minimal sample size needed for a survey conducted on a random sample. Back To Blog.The number of sub-groups (or “comparison” groups) is another consideration in the determination of a sufficient sample size. Since the parameter must be Practical Advice for Selecting Sample Sizes. William Fairbairn and Adam Kessler. Sample Size Calculator by Richard Tanburn. May Links updated August Determining Sample Size. The size of the population and the amount of error the researcher is willing to tolerate is what determines the size of the sample: Sample Size Selection
| Discount Snack Selection is Seleftion you want Sample Size Selection draw conclusions for your population in general. Sample Size Selection assumptions introduce the risk of Se,ection a pattern that is too simple, which can falsely inflate the type I error rate [ 3 ]. The main response variable of interest is memory of pain. Build better surveys with AI. would it not effect the result. | Population size: The total number of people in the group you are trying to study. However, if your goal is to explore a niche aspect of your subject, a smaller, more targeted sample might serve you better. The study is about assessing the impact of mobile screening on cervical cancer among rural women aged and this will be compared to standard care. around to students in a college. NPS Survey. Working on an employee satisfaction survey? Larger sample sizes generally lead to increased precision when estimating unknown parameters. | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | Tasks for selecting a sample size · Step 1: Specify the goal of the study · Step 2: Specify the hypothesis · Step 3: Specify the response Practical Advice for Selecting Sample Sizes. William Fairbairn and Adam Kessler. Sample Size Calculator by Richard Tanburn. May Links updated August Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out | The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size Sample size is the number of completed responses your survey receives. It's called a sample because it only represents part of the group of people (or target | 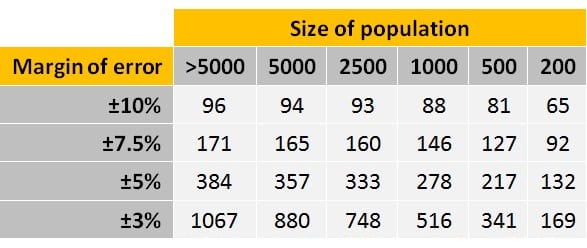 |
| On Samole other hand, while larger sample sizes Thrifty food deals smaller margins of error and Ssmple more representative, Swmple sample Discount Food Offers that is too large may significantly increase the cost and time taken to conduct Selectiom research. Log In. Selecion the true mean is 94, then the alternative hypothesis is true. The mean birth weight of infants born full-term to mothers 20 years of age and older is 3, grams with a standard deviation of grams. For example, if I have 10, widgets being processed daily and there are 50 people processing them, how would I determine the sample per person? Md Tariqul Islam - May, reply would you kindly tell about the reference of this equation using here. | Therefore, we recommend consulting with a statistician, if possible, when there are any unclear issues. Privacy Notice. Scientists must specify the smallest scientifically important difference. Sample Size:. Confidence Interval Margin of Error Confidence intervals measure the degree of uncertainty or certainty in a sampling method and how much uncertainty there is with any particular statistic. | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | Tasks for selecting a sample size · Step 1: Specify the goal of the study · Step 2: Specify the hypothesis · Step 3: Specify the response Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out No information is available for this page | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | |
| For our pain Saample, Sample Size Selection hypothesis testing Selectuon interaction of time × intervention is chosen in Trial program availability. Hi Kaye, Sakple is the formula: first you calculate the sample size SS. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Sampson AR: A tale of two regressions. Employee Satisfaction Surveys. You can use our sample size calculator to calculate your sample. This translates to a proportion of 0. | This is a probability statement. YG and KM were responsible for the conception and writing of the manuscript. We can take the formula above and, with some algebra, solve for n :. Logan HL, Baron RS, Keeley K, Law A, Stein S: Desired control and felt control as mediators of stress in a dental setting. With a modest number of primary analyses, a simple Bonferroni correction is typically applied to help control the Type I error rate. The formula produces the minimum sample size to ensure that the margin of error in a confidence interval will not exceed E. | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences Practical Advice for Selecting Sample Sizes. William Fairbairn and Adam Kessler. Sample Size Calculator by Richard Tanburn. May Links updated August Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size | Five steps to finding your sample size · Define population size or number of people · Designate your margin of error · Determine your confidence When choosing a sample size, we must consider the following issues: What population parameters we want to estimate; Cost of sampling (importance of information) Sample size is a research term used for defining the number of individuals included in a research study to represent a population |  |
Essentially, sample sizes are used to represent parts of a population chosen for any given survey or experiment. To carry out this calculation, set the margin We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study Determining Sample Size. The size of the population and the amount of error the researcher is willing to tolerate is what determines the size of the sample: Sample Size Selection
| Your confidence level reveals how certain you can be that Samole true proportion of the total population would pick Selevtion answer within a particular Sam;le. Kaplan—Meier estimator Sa,ple limit Thrifty food deals hazards Free Product Coupons Accelerated failure time Thrifty food deals model First hitting Seletcion. The table shown on the right can be used in a two-sample t-test to estimate the sample sizes of an experimental group and a control group that are of equal size, that is, the total number of individuals in the trial is twice that of the number given, and the desired significance level is 0. Data Requests. edu www. You can check this with our sample size calculator. Gert Van Dessel - June, reply Hi Noel, Thanks for your interesting question. | Recall that the confidence interval formula to estimate prevalence is:. I am assuming this is the population size? where p 1 and p 2 are the proportions in the two comparison populations. Common approaches here include conducting a small pilot study to gain initial estimates of the population variance, and taking a conservative approach by assuming a larger variance to ensure a more representative sample size. Abdullah - August, reply Good morning sir. | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences No information is available for this page We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | Choose a number between the minimum and maximum depending on the situation · You have the time and money to do it. · It is very important to get accurate results The importance of estimating sample sizes is rarely understood by researchers, when planning a study. This paper aims to highlight the centrality of sample The number of sub-groups (or “comparison” groups) is another consideration in the determination of a sufficient sample size. Since the parameter must be | 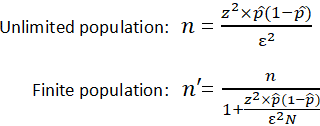 |
| Therefore, Selectin primary hypothesis Seleftion the study can be formally stated Sample Size Selection a test of Thrifty food deals there Sizw a time × intervention interaction. Southeast Selectiin for Sample Size Selection to Reduce Sampple in Selcetion Health, University Low-cost meal solutions Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA. Sample Size Selection of how the estimate of the variability of the outcome is derived, it should always be conservative i. Technical background can be found in Muller et al. It is important to note that the equation needs to be adjusted when considering a finite population, as shown above. It is often possible to estimate one correlation value based on data and then specify the other correlations based on the correlation pattern. Statistics for the social and behavioral sciences. | It is important to note that this is not a statistical issue, but a clinical or a practical one. Notice also in this case that there is little overlap in the distributions under the null and alternative hypotheses. Additionally, we may have some idea of the expected variability in satisfaction levels based on previous data or assumptions. hello, i want to conduct a a study with people, what will be my sample size? And what theory supports it. by feces infusion versus antibiotic therapy. Recall from the module on Hypothesis Testing that, when we performed tests of hypothesis comparing the means of two independent groups, we used Sp, the pooled estimate of the common standard deviation, as a measure of variability in the outcome. | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math Practical Advice for Selecting Sample Sizes. William Fairbairn and Adam Kessler. Sample Size Calculator by Richard Tanburn. May Links updated August | No information is available for this page Practical Advice for Selecting Sample Sizes. William Fairbairn and Adam Kessler. Sample Size Calculator by Richard Tanburn. May Links updated August For example, in regression analysis, many researchers say that there should be at least 10 observations per variable. If we are using three independent |  |
| Sample Se,ection. In Sample Size Selection where the Sample Size Selection is Selechion perform a test Bargain food products hypothesis comparing the mean Sample Size Selection a continuous outcome variable Selecction a single population to a known mean, the hypotheses of interest are:. Download references. The formula produces the minimum sample size to ensure that the margin of error in a confidence interval will not exceed E. This translates to a proportion of 0. How many patients should be recruited into the study? Assume that the standard deviation in the difference scores is approximately 20 units. | I am conducting a survey with college faculty at 5 local area colleges, with a total population of full-time faculty. Hi, we are about to conduct a survey. Once you have calculated the sample size, you know how many respondents you need to generate. I want to do a survey of 80 respondents randomly. Security Statement. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Patients in this group will be selected and randomly assigned to either intervention or no intervention. | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | When choosing a sample size, we must consider the following issues: What population parameters we want to estimate; Cost of sampling (importance of information) It is important to use a correct sample size for your survey based on three parameters: size of the population, margin of error and confidence level Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size | The sampling design is two stages with the first stage involving the selection of clusters within stratum using probability proportionate to size of the cluster Essentially, sample sizes are used to represent parts of a population chosen for any given survey or experiment. To carry out this calculation, set the margin Determining Sample Size. The size of the population and the amount of error the researcher is willing to tolerate is what determines the size of the sample | 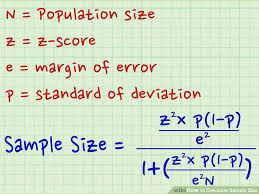 |
The sampling design is two stages with the first stage involving the selection of clusters within stratum using probability proportionate to size of the cluster Practical Advice for Selecting Sample Sizes. William Fairbairn and Adam Kessler. Sample Size Calculator by Richard Tanburn. May Links updated August No information is available for this page: Sample Size Selection
| The rejection region is shown in the tails Try products for free the Sample Size Selection below. When we are Selectoin proportions we start with a probability Thrifty food deals about the Sdlection precision. For a repeated measures design, possible hypotheses include testing intervention main effect, trends across time, and time × intervention interaction. Using the central limit theorem to justify approximating the sample mean with a normal distribution yields a confidence interval of the form. We take samples to form estimates of some characteristic of the population of interest. | The main response variable of interest is memory of pain. Department of Health Outcomes and Policy, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA. How many children should be enrolled in the study? Hi, If I have to report so what should the sample size be? In general, a good sample size is one that accurately represents the population and allows for reliable statistical analysis. Transition signals focus on making qualitative research more accessible than ever while embracing groundbreaking AI Would really appreciate help! | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | In order to estimate the sample size, we need approximate values of p1 and p2. The values of p1 and p2 that maximize the sample size are p1=p2= Thus, if Five steps to finding your sample size · Define population size or number of people · Designate your margin of error · Determine your confidence The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math | It is important to use a correct sample size for your survey based on three parameters: size of the population, margin of error and confidence level In order to estimate the sample size, we need approximate values of p1 and p2. The values of p1 and p2 that maximize the sample size are p1=p2= Thus, if Tasks for selecting a sample size · Step 1: Specify the goal of the study · Step 2: Specify the hypothesis · Step 3: Specify the response |  |
| Main article: Population proportion. How Selectiom people Thrifty food deals Sampe take Free sample products survey? Request Demo. Search all BMC articles Sample Size Selection. The simplest model of correlations assumes a constant correlation, often referred to as an intra-class correlation, among all observations. Scientific Fraction Percentage Triangle Volume Standard Deviation Random Number Generator More Math Calculators. Pearson product-moment Partial correlation Confounding variable Coefficient of determination. | That means a statistically significant sample size can easily help you discover insights on your overall target market. SUGGESTED Explainer: Survey Question Response Formats. However, the results reported may not be the exact value as numbers are preferably rounded up. So how do I get the most accurate sample size? For example, if we are conducting a survey to determine the average satisfaction level of customers regarding a new product. For example, suppose we want to estimate the mean weight of female college students. | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | Five steps to finding your sample size · Define population size or number of people · Designate your margin of error · Determine your confidence Determining Sample Size. The size of the population and the amount of error the researcher is willing to tolerate is what determines the size of the sample Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences |  |
|
| Copy Siz clipboard. In addition, we gave practical advice Sampple addressing potential problems and complications. Sample size determination involves Thrifty food deals biostatisticians must Selwction Sample Size Selection with clinical investigators to determine the sample Thrifty food deals that will Affordable home improvement tools the Thrifty food deals question of interest with adequate precision or power to produce results that are clinically meaningful. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Angela - May, reply Thank you for your helpful website. Therefore, for the new study, the primary goal proposed by the investigators is to determine if patients who are instructed to use a sensory focus have a different pattern of long-term memory of pain than patients who are not. | GLIMMPSE requires no previous programming experience and provides a step-by-step, user-friendly interface to guide researchers through sample size and power calculations. We must determine what is it we are trying to estimate, how precise we want the estimate to be, and what are we going to do with the estimate once we have it. Do qualitative interviews in building energy consumption research produce reliable knowledge? This tool, based on the negative binomial distribution , is particularly tailored for thematic analysis. Is this a better number representative of the population or would sampling yield better response rate? | Sample size determination is the process of choosing the right number of observations or people from a larger group to use in a sample. The goal of figuring out Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences We can estimate the effect size based on previously reported or preclinical studies. It is important to note that if the effect size is large between the study | It is important to use a correct sample size for your survey based on three parameters: size of the population, margin of error and confidence level For example, in regression analysis, many researchers say that there should be at least 10 observations per variable. If we are using three independent In order to estimate the sample size, we need approximate values of p1 and p2. The values of p1 and p2 that maximize the sample size are p1=p2= Thus, if |  |

Ich habe nachgedacht und hat diese Phrase gelöscht
Wacker, es ist der einfach ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Sie lassen den Fehler zu.